本文不保证读者能都读懂。写本文的主要目的是测试数学公式功能,文字讲解基本没有,请谨慎阅读。
傅里叶变换
连续傅里叶变换是一个 \(\mathbb R \rightarrow \mathbb C\) 到 \(\mathbb R \rightarrow \mathbb C\) 的变换。
\[ \mathcal F \left[f \right] = \hat{f}(\xi) = \int_{-\infty}^\infty f(x)\ e^{- 2\pi i x \xi}\,dx (\xi \in \mathbb C) ......\left(1\right)\]
它的作用是对于一个时域的复数函数,求出其频谱。
当自变量x表示时间(以秒为单位),变换变量ξ表示频率(以赫兹为单位)。在适当条件下,\(\hat f\)可由逆变换(inverse Fourier transform)由下式确定f:
\[ \mathcal F^{-1} \left[\hat f \right] = f(x) = \int_{-\infty}^\infty \hat f(\xi)\ e^{2 \pi i \xi x}\,d\xi (x \in \mathbb R)......\left(2\right)\]
它的作用是对于一个频域的复数函数,求出其时域表示。
离散傅里叶变换(DFT)
考虑将上述 \(f\) 及 \(\hat f\) 函数,将它们离散取值。考虑数列 \(g\) 及 \(\hat g\) ,下标\(x \in \left[0, n \right]\),则将上\((1),(2)\)式适当变形得
\[ \mathbf F \left[g \right] = \hat{g}(n)= \frac{1}{\sqrt N} \sum_{k=0}^{N-1} g(k) e^{-2\pi i\frac{kn}{N}} ......\left(1, Decrete,Normalized \right)\]
\[ \mathbf F^{-1} \left[\hat g \right] = {g}(k)= \frac{1}{\sqrt N} \sum_{n=0}^{N-1} \hat g(n) e^{2\pi i\frac{kn}{N}} ......\left(2, Decrete,Normalized\right)\]
以上两个变换有一种美妙的性质:都符合卷积定理,即可以将某一个域内的卷积对偶于其对应域内的乘法。
为了简化起见,可以将\(\left(1, D,N\right)\) \(\left(2, D,N\right)\)两式改变一下常数项,得到非正则化的以下两式,不改变主要性质。
\[ \mathbf F \left[g \right] = \hat{g}(n)= \sum_{k=0}^{N-1} g(k) e^{-2\pi i\frac{kn}{N}} ......\left(1, Decrete \right)\]
\[ \mathbf F^{-1} \left[\hat g \right] = {g}(k)= \frac{1}{N} \sum_{n=0}^{N-1} \hat g(n) e^{2\pi i\frac{kn}{N}} ......\left(2, Decrete\right)\]
为了方便起见,设符合方程 \(x^N=1\) 的复数 \(x\) 称为 \(N\) 次单位复根。共有\(N\)个,符合下式:
\[x = W_N^{n} = e^{2\pi \frac{n}{N}} \]
单位复根有以下性质:
\[W_{aN}^{an} = W_N^{n}\] \[W_N^{n} = {(W_N^{-n})}^{*}\] \[W_N^{n} = W_N^{n+rN},r\in \mathbb N\]
那么,从矩阵角度考察\(DFT\)。
\[\mathbf F = \begin{bmatrix}1 &1 &1 &\cdots &1\\\\ 1 &W_N^{-1} &W_N^{-2} &\cdots &W_N^{-(N-1)}\\\\ 1 &W_N^{-2} &W_N^{-4} &\cdots &W_N^{-2(N-1)} \\\\ \vdots &\vdots &\vdots &\ddots &\vdots\\\\ 1 &W_N^{-(N-1)} &W_N^{-2(N-1)} &\cdots &W_N^{-(N-1)^2}\end{bmatrix}......(1, MatrixForm)\]
\[\mathbf {F}^{-1} = \frac{1}{N} \begin{bmatrix} 1 &1 &1 &\cdots &1\\\\ 1 &W_N^1 &W_N^2 &\cdots &W_N^{N-1}\\\\ 1 &W_N^2 &W_N^4 &\cdots &W_N^{2(N-1)} \\\\ \vdots &\vdots &\vdots &\ddots &\vdots\\\\ 1 &W_N^{N-1} &W_N^{2(N-1)} &\cdots &W_N^{(N-1)^2}\end{bmatrix}......(2, MatrixForm)\]
显然,以上两矩阵互逆。
考察矩阵1,\(F_{kn}=W_N^{kn}\),那么
\[F=F^T\] 即,沿主对角线对称
\[F_{(2r)n} = F_{(2r)(n+\frac{N}{2})}\] 即,偶数行的左半部分与右半部分相等
\[F_{(2r+1)n} = W_N^{\frac{2}{N}} *F_{(2r+1)(n+\frac{N}{2})} = -F_{(2r+1)(n+\frac{N}{2})}\] 即,奇数行左右半部分互为相反数
那么考虑, \[ \mathbf F \left[g \right] = \hat{g}(n)= \sum_{k=0}^{N-1} g(k) W_N^{-kn} = \sum_{k=0}^{\frac{N}{2}-1} g(k) W_N^{-kn}+\sum_{k=\frac{N}{2}}^{N-1} g(k) W_N^{-kn} \]
\[= \sum_{k=0}^{\frac{N}{2}-1} g(k) W_N^{-kn}+\sum_{k=0}^{\frac{N}{2}-1} g(k+\frac{N}{2}) W_N^{-k(n+\frac{N}{2})}\]
对 \(\hat g\) 奇偶分开讨论,
\[ \hat g (2r) = \sum_{k=0}^{\frac{N}{2}-1}\Big(g(k)+g(k+\frac{N}{2})\Big)W_{\frac{N}{2}}^{-rk}\]
即,原矩阵的这些位置 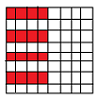 等于一个\(N/2\)规模的DFT矩阵。
等于一个\(N/2\)规模的DFT矩阵。
\[ \hat g (2r+1) = \sum_{k=0}^{\frac{N}{2}-1}\Big(g(k)-g(k+\frac{N}{2})\Big)W_N^{-k}W_{\frac{N}{2}}^{-rk}\]
这样就得到了两个\(\frac{N}{2}\)点DFT。
不断分治,就得到了一个\(O(N \log_2 N)\)的做法。
C++代码
typedef complex<double> T;
T dwg(int n, int flag)
{
return T(cos(pi * 2 / n), flag * sin(pi * 2 / n));
}
void fft(T *a, int m, int flag) // 求2^m点FFT
{
int nn = 1 << m;
while (m) {
int n2 = 1 << (m - 1);
int n = n2 << 1;
T wn(dwg(n, -flag));
for (int j = 0; j < nn; j += n) {
T w = 1;
T *l = a + j, *r = a + n2 + j;
T *rb = a + n + j;
T t;
for (; r < rb; ++l, ++r, w *= wn) {
t = *l - *r;
*l += *r;
*r = t * w;
}
}
--m;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { // 位反转
if (R[i] > i) {
swap(a[i], a[R[i]]);
}
}
}对于正向FFT,取\(flag = 1\);对于逆FFT,取\(flag = -1\)。
例题
#include "bits/stdc++.h"
using namespace std;
const int BUF_SIZE = (int)1e6 + 10;
struct fastIO
{
char buf[BUF_SIZE];
int cur;
FILE *in, *out;
fastIO()
{
cur = BUF_SIZE;
in = stdin;
out = stdout;
}
inline char nextChar()
{
if (cur == BUF_SIZE) {
fread(buf, BUF_SIZE, 1, in);
cur = 0;
}
return buf[cur++];
}
inline int nextInt()
{
int x = 0;
char c = nextChar();
while (!('0' <= c && c <= '9')) c = nextChar();
while ('0' <= c && c <= '9') {
x = x * 10 + c - '0';
c = nextChar();
}
return x;
}
inline void printChar(char ch)
{
if (cur == BUF_SIZE) {
fwrite(buf, BUF_SIZE, 1, out);
cur = 0;
}
buf[cur++] = ch;
}
inline void printInt(int x)
{
if (x >= 10) printInt(x / 10);
printChar(x % 10 + '0');
}
inline void close()
{
if (cur > 0) {
fwrite(buf, cur, 1, out);
}
cur = 0;
}
} fin, fout;
const int lg2maxn = 18;
const int maxn = (1 << lg2maxn);
const double pi = acos(-1);
namespace nscpx
{
typedef double T;
struct cpx
{
T x, y;
cpx(T a = 0, T b = 0):x(a), y(b) {}
cpx operator-() const
{
return cpx(-x, -y);
}
cpx &operator+=(const cpx &a)
{
x += a.x;
y += a.y;
return *this;
}
cpx &operator-=(const cpx &a)
{
x -= a.x;
y -= a.y;
return *this;
}
cpx &operator*=(const cpx &a)
{
T nx;
nx = x * a.x - y * a.y;
y = y * a.x + x * a.y;
x = nx;
return *this;
}
cpx operator+(const cpx &a) const
{
return cpx(x + a.x, y + a.y);
}
cpx operator-(const cpx &a) const
{
return cpx(x - a.x, y - a.y);
}
cpx operator*(const cpx &a) const
{
return cpx(x * a.x - y * a.y, x * a.y + y * a.x);
}
};
}
using nscpx::cpx;
int R[maxn];
typedef cpx T;
T dwg(int n, int flag)
{
return T(cos(pi * 2 / n), flag * sin(pi * 2 / n));
}
void ffft(T *a, int m, int flag)
{
int nn = 1 << m;
while (m) {
int n2 = 1 << (m - 1);
int n = n2 << 1;
T wn(dwg(n, -flag));
for (int j = 0; j < nn; j += n) {
T w = 1;
T *l = a + j, *r = a + n2 + j;
T *rb = a + n + j;
T t;
for (; r < rb; ++l, ++r, w *= wn) {
t = *l - *r;
*l += *r;
*r = t * w;
}
}
--m;
}
}
void rev(T *a, int m)
{
int n = 1 << m;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (R[i] > i) {
swap(a[i], a[R[i]]);
}
}
}
int n, m;
T a[maxn], b[maxn];
#define lowbit(x) ((x)&-(x))
int main()
{
n = fin.nextInt();
m = fin.nextInt();
int maxnn = m + n + 1;
while (maxnn != lowbit(maxnn)) maxnn += lowbit(maxnn);
int shit = 0;
while (maxnn > (1 << shit)) ++shit;
assert(maxnn == (1 << shit));
for (int i = 0; i < maxnn; ++i) {
R[i] = (R[i >> 1] >> 1) | ((i & 1) << (shit - 1));
}
for (int i = 0; i <= n; ++i) {
a[i].x = fin.nextInt();
}
for (int i = 0; i <= m; ++i) {
b[i].x = fin.nextInt();
}
ffft(a, shit, 1);
ffft(b, shit, 1);
for (int i = 0; i < maxnn; ++i) {
a[i] *= b[i];
}
rev(a, shit);
ffft(a, shit, -1);
rev(a, shit);
fout.cur = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= (n + m); ++i) {
fout.printInt(a[i].x / maxnn + 0.5);
fout.printChar(' ');
}
fout.printChar('\n');
fout.close();
return 0;
}钦此。